Reaction Intermediates
Reaction Intermediates: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Reaction Intermediates, Carbanions, Carbene & Benzyne etc.
Important Questions on Reaction Intermediates
Correct order of rate hydrolysis or rate of reaction towards AgNO3 for following compounds is:
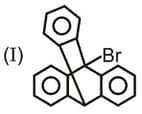
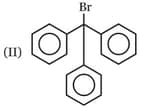
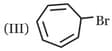
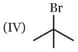
Which one of the following carbonyl compound when treated with dilute acid forms the more stable carbocation?
The abstraction of proton will be fastest from which carbon in the following compound?
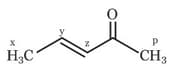
Write correct order of stability of following carbocations :
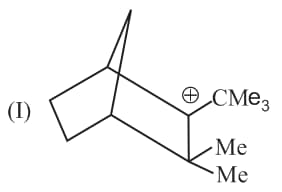
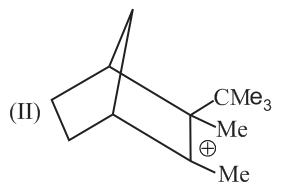
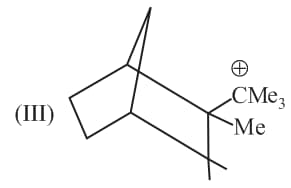
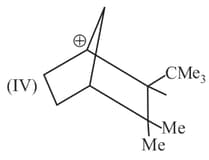
Rank the following free radicals in order of decreasing stability:
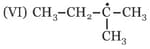
The correct stability order for the following species is
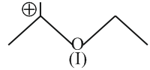
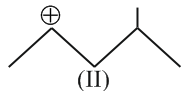
An organic reaction occurs through making and breaking of bonds. The breaking of bonds may occur either homolytically leading to the formation of radicals or heterolytically generating positively and negatively charged species. The neutral species (free radicals, carbenes, nitrenes, etc.) and positively charged species being electron deficient are collectively called electrophiles while neutral and negatively charged species which are electron rich are called nucleophiles. An organic reaction usually involves the attack of a reagent (radicals, positively and negatively charged species) on the substrate molecule). The substrate molecule, although as a whole electrically neutral, has centers of low and high electron density due to displacement of bonding electrons. These electron displacements occur through inductive, electromeric, resonance and hyperconjugation effects. Whereas inductive effects involve displacement -electrons, resonance effects involve transfer of - and -electrons along a conjugated system. Hyperconjugatlon effects, on the other hand, involve --conjugation. Both inductive and hyperconjugation effects can be used to explain the stability of carbocations and free radicals which follow the stabilIty order : . The stability of carbanions, however, follows opposite order.
The stability of a molecule can be judged on the basis of contribution of its resonance structures. Resonance structures have same position of nuclei and have the same number of unpaired electrons. Among resonance structures, the one which has greater number of covalent bonds, has less separation of opposite charges, a negative charge on more electronegative and a positive charge on a more electropositive atom are more stable than others.
The geometry of a carbocation is _____.
Triplet state of Reaction intermediates like carbene & nitrene are more stable than their singlet state. This fact can be explained on the basis of
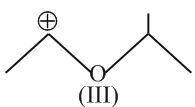
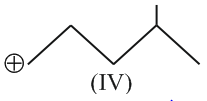
The stability of carbanions
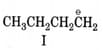
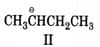
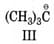
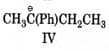
follows the order
Which of the following is a suitable condition for homolytic bond fission?
Which of the following compounds has planar geometry?
What is the geometry of methyl free radical?
Which is the least stable free radical?
Which is the most stable free radical?
_____ are formed by the homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond.
The stability of the free radicals due to inductive effect follows the order,
Explain the stability of free radicals due to inductive effect.
The correct order of increasing stabilities of the following carbocations.
(i) Allyl carbocation
(ii) Ethyl carbocation
(iii) Benzyl carbocation
(iv) Isobutyl carbocation
Explain the factors that affect the stability of the carbanion.
State the hybridisation of carbanion.
